• Because the energy of the two electrons is lower than the energy of the individual atoms, the molecule is stable. Figure 9.26: (a) The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the H2 molecule. (b) The shapes of the molecular orbitals are obtained by squaring the wave functions for MO1 and...This second orbital is therefore called an antibonding orbital. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+.Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the #1s# orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons.the valence molecular orbital diagram for the anion B2- is given. Which of the following options correctly interpret this diagram? - B2- has a shorter - the MO diagram shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each MO - The MO diagram can be used to calculate bond order and predict...The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p Experiments have shown that O2 and F2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but B2, C2, and N2 are best...
Tutorial on Chemical Bonding, Part 8 of 10 (Molecular orbitals)
A molecular orbital is an allowed spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular orbital energy. Use a qualitative molecular orbital energy-level diagram to predict the valence electron configuration, bond order, and likely existence of the Na 2 − ion.365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Determine whether each is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. a. H2 B.O. = 1 stable diamagnetic b. He2 ∗ σ1s σ1s ∗ σ1s c. O2 B.O. = 2 stable paramagnetic π ∗2p ∗ σ2p π 2p σ1s...Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12.Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top.
What is the molecular orbital diagram for B_2? | Socratic
molecular orbital theory b2 this video shows the end of the be2 molecule mo diagram and explains pi orbitals paramagnetism and the mo diagrams for b2 diagram tricks for molecular orbital theory part i jee aiims neet xi xii duration 40 30 er dushyant kumar b tech iit roorkee 437 002 views The difference...A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of mol...The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2, O2, F2, and Ne2.This video shows the end of the Be2 molecule MO diagram and explains pi orbitals, paramagnetism, and the MO diagrams for B2.The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The MOs for the valence orbitals of the second period are shown in Figure 8.37. Looking at Ne2 molecular orbitals, we see that the order is consistent with the generic diagram...
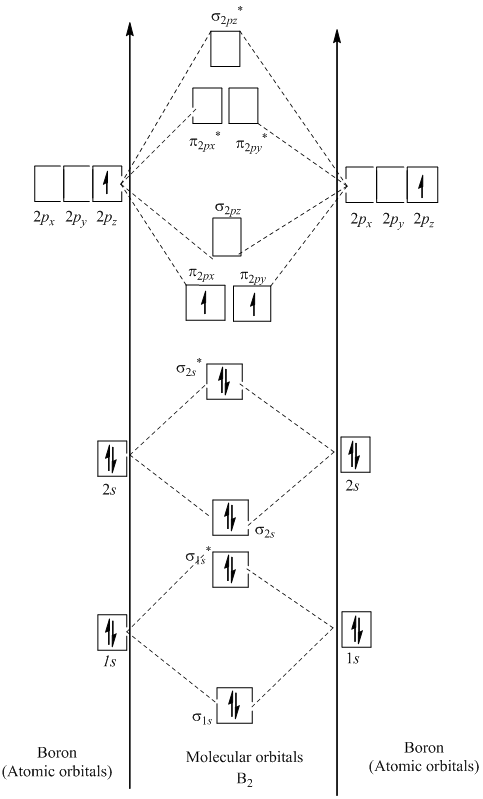
Before we will draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we should in finding the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combos for boron's atomic orbitals.
Then we rank them in order of increasing power.
We can forget about the #1s# orbitals, because they don't comprise the valence electrons.
Each boron atom has one #2s# and 3 #2p# valence orbitals.
The #2s# orbitals will overlap to form #2sσ# and #2sσ"*"# orbitals.
The #2p_x# orbitals can overlap end-on to form #2pσ# and #2pσ"*"# orbitals.
The #2p_y# and #2p_z# orbitals can overlap side-on to shape degenerate pairs of #2pπ# and #2pπ"*"# orbitals.
The order of energies is #2sσ < 2sσ^✳ < 2pπ < 2pσ < 2pπ^✳ < 2pσ^✳#.
We have 3 valence electrons from each B atom, so B₂ will have six valence electrons.
We use the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund's rule to fill the orbitals in an Aufbau process.
The molecular orbital diagram for B₂ then becomes
The video under describes find out how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for B₂ and different diatomic molecules from Row 2 components of the Periodic Table.
[embedded content material]
Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Is Most Stable. A.... - HomeworkLib

Valence Bond Theory – H2 Valence Bond Theory – F2 Valence Bond Theory – HF Conformations Double And Triple Bonds
Lecture 32 (1)
CHMA10H3 Lecture Notes - Fall 2014, Lecture 30 - Molecular Orbital Diagram, Microsoft Onenote, Pauli Exclusion Principle

Combo With "inorganic Exam 2" And 2 Others Flashcards | Quizlet

Molecular Orbital Analysis Of The Bonding In Low Nuclearity Gold And Platinum Tertiary Phosphine Complexes And The Development O
A. Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Is Paramagnetic. B_2^2+, B2, C_2^2-, B_2^2- And N_2^2+ B. Draw The Lewis Structures And Molecular Orbital Diagrams For |

Molecular Orbitals In Inorganic Chemistry
Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn General Wiring Diagram - Free Photos
Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory
Solved: Place The Species B2+, B2, And B2− In Order Of Increasi... | Chegg.com
How To Explain The Excited States In The Dinitrogen Cation? - Chemistry Stack Exchange

Question 1) By Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams For B2, C2, N2, O2, And F2, Predict Which... - HomeworkLib

Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory

ENERGY LEVELS FOR HOMONUCLEAR DIATOMIC MOLECULES What Do I Have To Know? You Will Be Responsible For Being Able To Write Or
Hwk11_che103 _Soln
Multiple Bonds - Bond Energies & Lengths - Molecular Orbital Theory - General Chemistry Lecture 1140 - Dr. Sundin - UW-Platteville

Complete This Valence Molecular-orbital Diagram For Oxygen, O2. Click The Blue Boxes To Add Electrons As... - HomeworkLib

Molecular Orbitals – Introductory Chemistry – 1st Canadian Edition

Molecular Structure And Labeling Diagram Of 2 (Cp* Ligands Are Omitted... | Download Scientific Diagram

Synthesis, Structure, Bonding, And Reactivity Of Metal Complexes Comprising Diborane(4) And Diborene(2): [{Cp*Mo(CO)2}2{μ‐η2:η2‐B2H4}] And [{Cp*M(CO)2}2B2H2M(CO)4], M=Mo,W - Mondal - 2018 - Angewandte Chemie - Wiley Online Library
![Synthesis, Structure, Bonding, And Reactivity Of Metal Complexes Comprising Diborane(4) And Diborene(2): [{Cp*Mo(CO)2}2{μ‐η2:η2‐B2H4}] And [{Cp*M(CO)2}2B2H2M(CO)4], M=Mo,W - Mondal - 2018 - Angewandte Chemie - Wiley Online Library Synthesis, Structure, Bonding, And Reactivity Of Metal Complexes Comprising Diborane(4) And Diborene(2): [{Cp*Mo(CO)2}2{μ‐η2:η2‐B2H4}] And [{Cp*M(CO)2}2B2H2M(CO)4], M=Mo,W - Mondal - 2018 - Angewandte Chemie - Wiley Online Library](https://i0.wp.com/onlinelibrary.wiley.com/cms/asset/421931a0-a961-4a1f-b02b-52fd14f00ca9/ange201803154-fig-0002-m.jpg)
0 comments:
Post a Comment